Assistant IA DPO

DPO, optimisez votre temps de travail grâce à notre assistant IA
⏳ Gagnez jusqu’à 2H par jour
💰 100% Gratuit
Ce qui vous demandait des heures ne prend plus que quelques minutes.
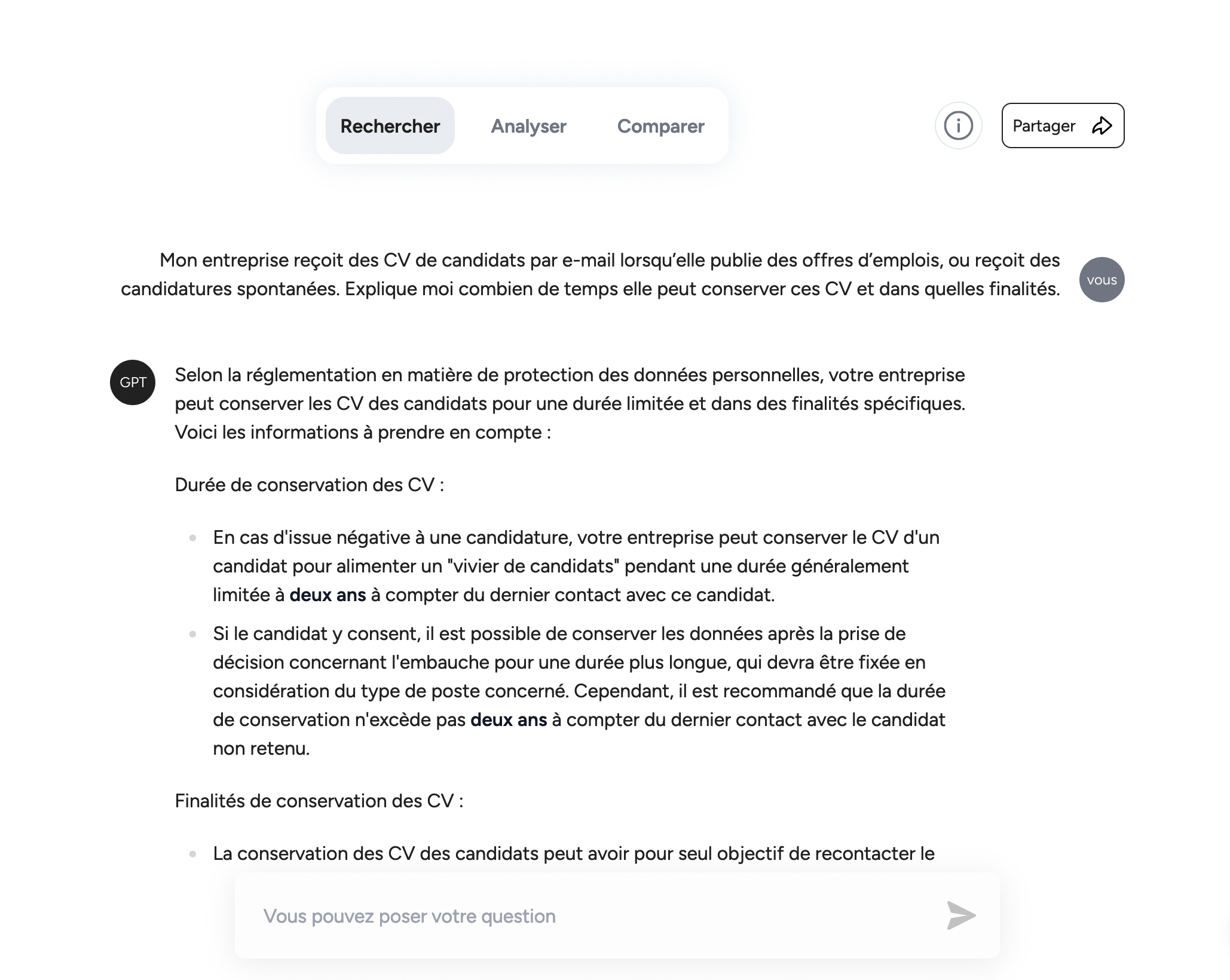
Gagnez 80 % du temps de votre recherche juridique
Olympe propose un moteur de recherche qui vous permet de trouver l’information juridique et technique pertinente en quelques secondes.
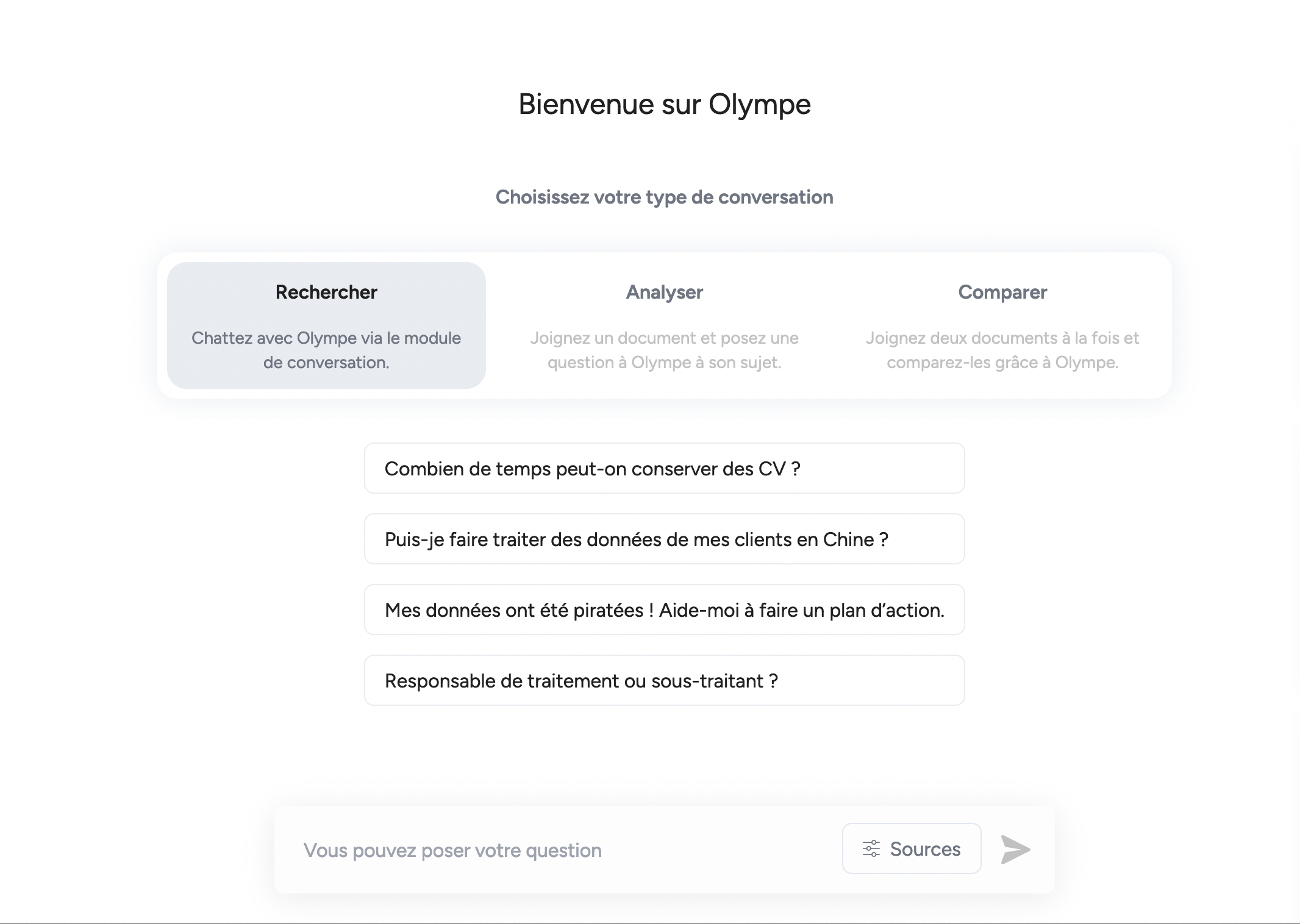
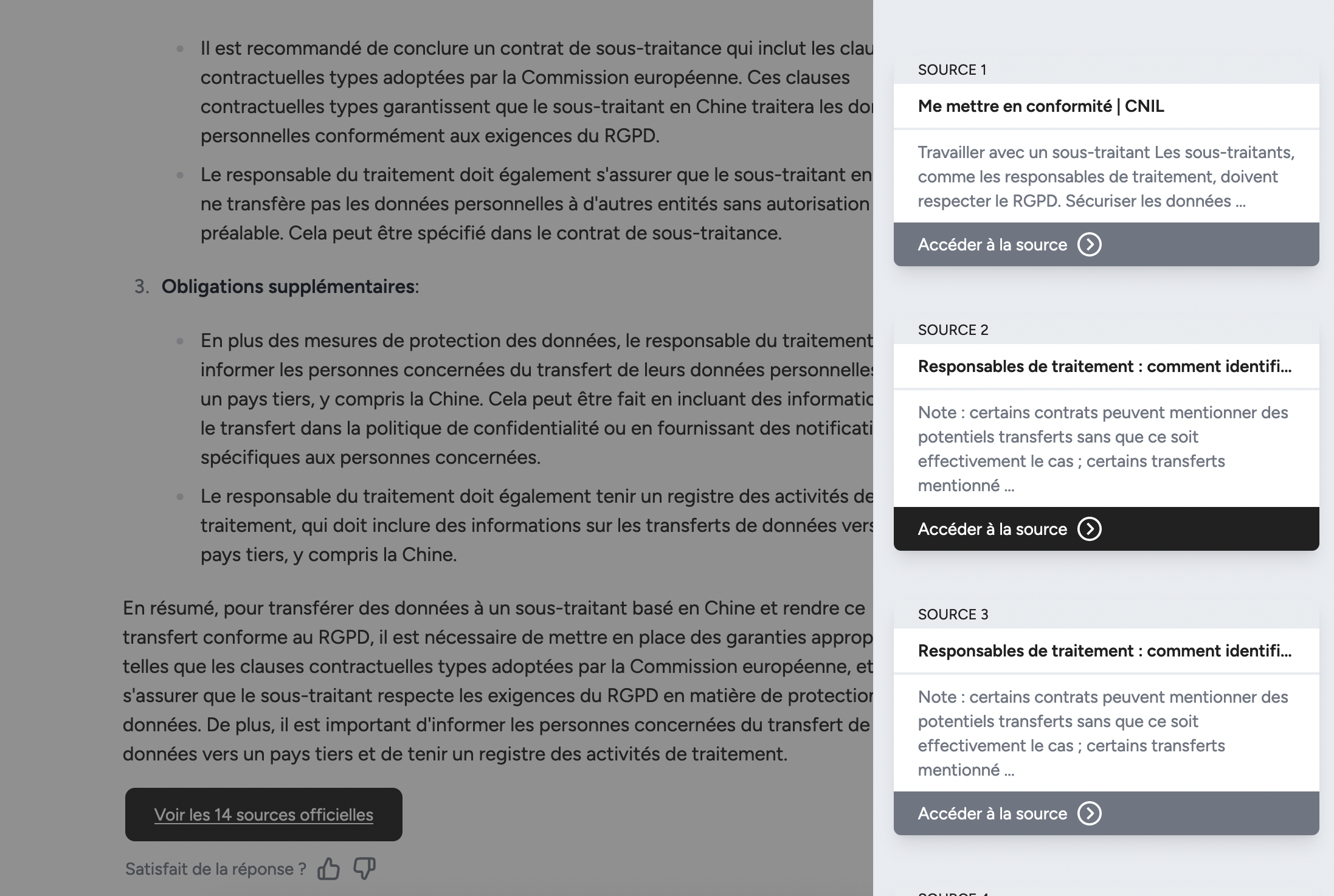
Appuyez vos réponses grâce à des sources fiables
Olympe vous répond en citant ses sources et vous permet de rédiger des réponses pertinentes rapidement.
Accédez aux sources et consultez-les en un clic.
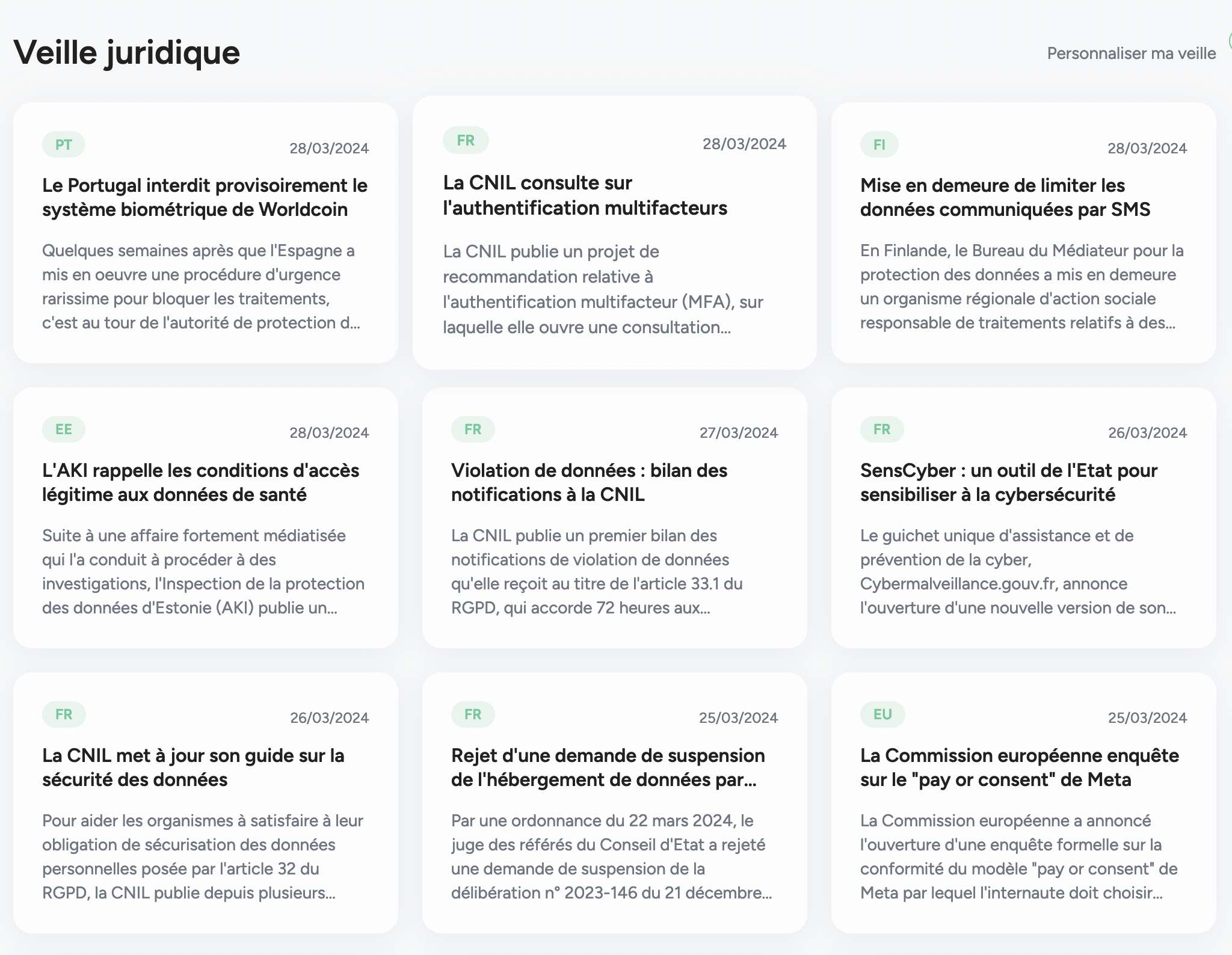
Une veille juridique à la pointe de l’actualité
Rejoignez les 1000+ cabinets et DPOs déjà inscrits
Environ 20 heures
par semaine gagnées
de marge gagnés
DPO & cabinets utilisateurs quotidien
Audit RGPD effectués
Contactez-nous
CGU – Olympe App
Politique de confidentialité – Olympe App
Mentions légales – Olympe App
DPA – Olympe App
CGU – Olympe.legal
Politique de confidentialité – Olympe.legal
Mentions légales – Olympe.legal
Legal Index